Custom scripts in the Explorer
Use preflight and postflight scripts to manage auth flows and test response data
The GraphOS Explorer can run custom scripts when executing each GraphQL operation, similar to tools like Postman. These JavaScript-based scripts can get and set the values of
Preflight scripts are useful for managing authentication flows like OAuth, for example, by refreshing an expired access token. Postflight scripts are useful for validating workflows that depend on response data.
Script types
The Explorer lets you define two different types of scripts:
- Preflight scripts: You can define a single preflight script per variant of a graph. This script runs before every Explorer operation that's executed against the associated variant.
- Preflight scripts are helpful for enabling organization-wide Explorer authentication to your graph.
- Operation scripts: If you useoperation collections, you can define one pre- and one post-operation script for each saved operation in a collection.
- Pre-operation scripts run before the operation executes. They act as additional, per-operation, preflight scripts.
- Post-operation scripts run after the operation executes. They act as per-operation postflight scripts.
- Operation scripts are helpful for testing or debugging the behavior of individual operations or operation chains.
Script execution order
If you define and use all possible scripts for an operation, the order is as follows:
Important considerations for Explorer scripts
Scripts are stored in the Apollo cloud in plaintext.
⚠️ CAUTION
Do not include secret credentials in scripts. Instead, team members can provide their individual credentials to the Explorer via
environment variables.If a team member has view access to a particular graph variant or operation collection, that team member can also view any scripts associated with that variant or operation collection.
Preflight scripts are on by default. Individual team members can
turn them offfor their own Explorer usage.Operations scripts are off by default. Individual team members can
turn them onfor their own Explorer usage.
Preflight scripts
Add preflight scripts
ⓘ NOTE
For
For non-protected variants, members with the Contributor role can also modify the preflight script.
To create a preflight script:
- Open GraphOS Studioand then open the Explorer for the graph and variant you want to create a script for.
Open the Explorer's Settings tab and scroll down to the Preflight Script.
Click + Add script. A script editor dialog appears.
Click Show snippets on the bottom left of the editor to display a list of common helpful actions you can perform from your preflight script. Examples include sending HTTP requests and interacting with Explorer environment variables.
Develop your script in the Script editor panel. As you develop, you can click Test script to test its execution. Console messages are printed in the Console output panel.
When your script is ready, click Save. Studio stores your script.
That's it! After you save your script, it's automatically loaded for any team member that uses the Explorer with the associated variant.
Turn off preflight scripts
By default, a variant's preflight script runs automatically before every GraphQL operation that's executed in the Explorer. Team members can turn off the script for their individual Explorer usage from the Personal Settings > Scripts section of the Explorer's Settings tab. To do so, toggle the Preflight script switch to OFF.
Operation scripts
Add operation scripts
ⓘ NOTE
You can only create operation scripts for operations that are saved in an
Only organization members
From the Explorer, open an operation from the Operation Collections menu:
From the Explorer's bottom panel, select the Pre-Operation Script or Post-Operation Script tab and click + Add Script. A script creation dialog appears.
Create, test, and save your script.
- For details on script creation, see steps 4 and 5 of Add preflight scripts.
- Click Test script to test your script before saving it.
- For details on script creation, see steps 4 and 5 of
After you save an operation script, make sure to
Mocking responses for post-operation scripts
The operation script modal has a Mocked Operation Response area so you can test post-operation scripts before saving them. Scripts can access any JSON GraphQL response you add in the Mocked Operation Response via the explorer.response.body
Turn on operation scripts
By default, operation scripts are off for each individual team member. Team members can turn on operation scripts for their individual Explorer usage from the Personal Settings > Scripts section of the Explorer's Settings tab. To do so, toggle the Operation script switch to ON.
Chaining operations
A script can use the explorer.runOperationexplorer.runOperation.
You can use this mechanism to chain together a sequence of operations for more advanced workflows.
Scripting API reference
These symbols are available within the scope of both preflight scripts and operation scripts. Snippets for these symbols are available via the Show snippets link in the scripting modal.
| Name / Type | Description |
|---|---|
explorer.environment.get
| Function that returns the current value of the environment variable with the specified |
explorer.environment.set
| Function that sets a new value for the environment variable with the specified |
explorer.fetch
| Function for making HTTP requests to external services from within a script. Network requests are initiated from an origin of |
explorer.runOperation
| Function for executing other saved operations. If the target operation has defined its own script, it will run before its operation.
|
explorer.prompt
| Function that prompts the user for input and returns the value in a promise. If the user cancels the prompt, the promise resolves to The prompt supports Markdown rendering of the |
explorer.oauth2Request
| Function that prompts the user to authenticate using your OAuth 2.0 provider's URL (specified by This function returns a promise containing the query parameters from your OAuth provider's response. If the user cancels the prompt, the promise resolves to For OAuth 2.0 authentication to work with the Explorer, your OAuth 2.0 provider must recognize |
explorer.request.body
| The body of the |
explorer.response.body
| The JSON representation of the GraphQL operation response. Used in |
explorer.CryptoJS | This exposes the |
Examples
Get an environment variable
Scripts can access an environment variable
const secretToken = explorer.environment.get("token");
Set an environment variable
The following example runs an operation and sets an environment variable for use in future operations:
const response = await explorer.runOperation({scope: "shared",graphRef: "SpaceX-pxxbxen@current",collectionName: "Mission Control",operationName: "Ships",});const firstShipID = response.result.data.ships[0].id;explorer.environment.set("shipID", firstShipID);
Authenticate using an authorization provider URL
The following example uses the explorer.oauth2Request
const responseQueryParams = await explorer.oauth2Request('http://yourauthprovider.com/authorize',{client_id: "",state: "",scope: "openid",response_type: "code",code_challenge_method: "S256",code_challenge: "",code_verifier: "",})
See the following example for how you can use the response from a explorer.oauth2Request
Set an authorization environment variable
The following example uses the explorer.environment.set
let futureDate = explorer.environment.get('futureDate');const now = Date.now();if (!futureDate || now >= futureDate ) {const authUrl = 'https://<customerdomain>.okta.com/oauth2/<customerid>/v1/authorize';const qp = {client_id: <clientid>,state: "abc",scope: "openid",response_type: "token",code_challenge_method: "S256",nonce: "nonce"};const result = await explorer.oauth2Request(authUrl, qp);const token = result.access_token;explorer.environment.set('Authorization', {token});const nowDate = new Date();futureDate = new Date(nowDate.getTime() + (1 * 55 * 1000));explorer.environment.set('futureDate', futureDate.getTime());}
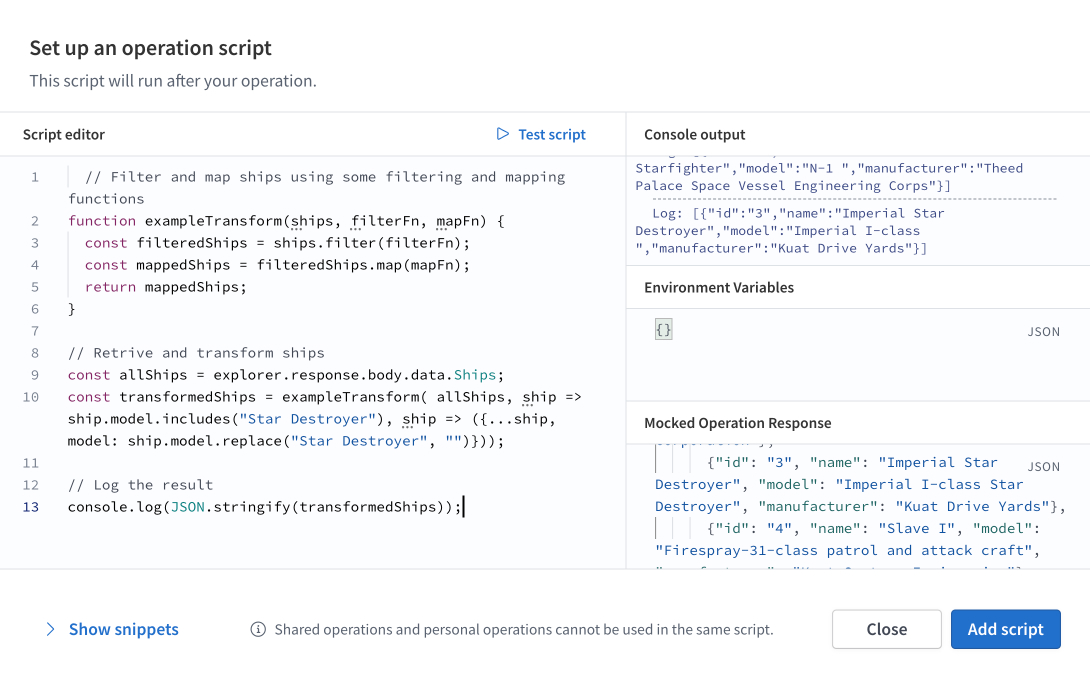
Transform and log response data
You can use a post-operation script to filter, map, or otherwise transform response data and log it. This can be helpful when a request returns numerous results in the response.
For example, imagine you have a query called Ships:
query Ships {idnamemodelmanufacturer}
The corresponding response might look like this:
{"data": {"Ships": [{"id": "1","name": "Millennium Falcon","model": "YT-1300 Light Freighter","manufacturer": "Corellian Engineering Corporation"},{"id": "2","name": "X-wing Starfighter","model": "T-65 X-wing","manufacturer": "Incom Corporation"}// ... (thousands of ships)]}}
You can use a post-operation script to access, transform, and log the returned results:
// Filter and map ships using some filtering and mapping functionsfunction exampleTransform(ships, filterFn, mapFn) {const filteredShips = ships.filter(filterFn);const mappedShips = filteredShips.map(mapFn);return mappedShips;}// Retrive and transform shipsconst allShips = explorer.response.body.data.Ships;const transformedShips = exampleTransform( allShips, filterFn, mapFn);// Log the resultconsole.log(transformedShips);
You can view the logged results in the Console output section of the Explorer.
ⓘ NOTE
You can view the output from console.logs in the Console output while writing and testing scripts. To see and interact with logged items when running an operation in Explorer, open your browser's devtools.